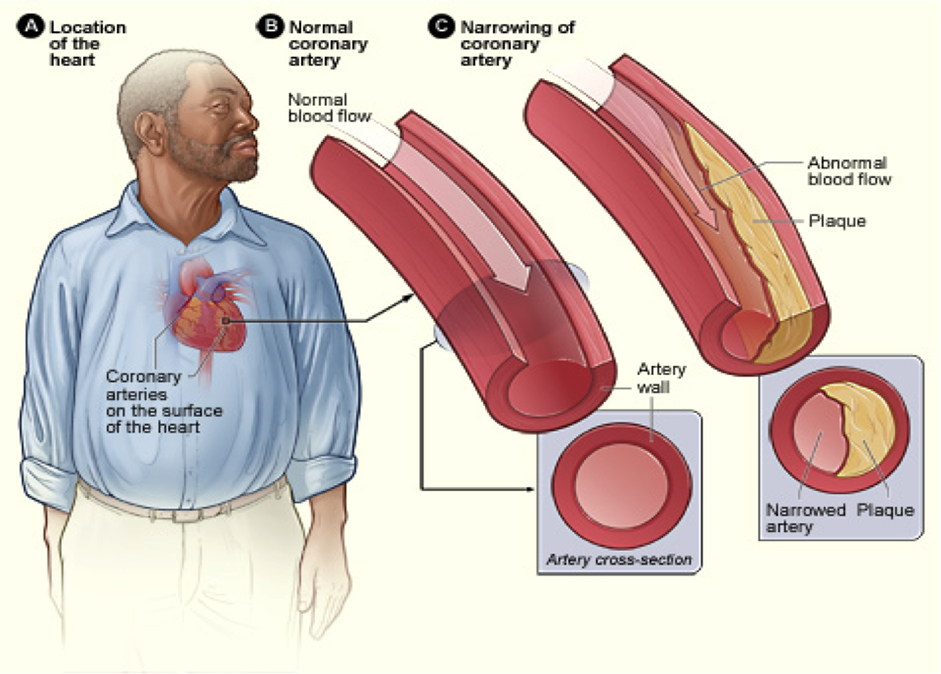
Is a disease in which a waxy substance called plaque builds up inside the coronary arteries which occurs over the course of many years.
SYMPTOMS
➢ Shortness of breath
➢ Irregular heart beat
➢ Heart failure where the heart fails to pump blood around the body as well as it used to because it has been damaged e.g. after a heart attack
➢ Occasionally feels like a heartburn
➢ Angina or chest pains which causes a tightness and heaviness in the centre of the of the chest and spreads to the arms, neck, jaw, back and stomach
➢ Heart attack where the arteries become fully blocked (myocardial infarction)
PREVENTIVE MEASURES
➢ Eating a healthy balanced diet that composes of:
o Low fat mostly unsaturated fats like sunflower oil, avocado, nuts, seeds
o Fruits, vegetables and foods that are high in fibre
o Low amounts of salt and sugar
➢ Being physically active as exercise reduces chances of getting BP and lowers cholesterol
➢ Stop smoking. Cigarettes damage the lining of the blood vessels, increases fatty deposits in the arteries, increases clotting, raises LDL cholesterol and promotes coronary artery spasm. Nicotine also accelerates the heart rate and raises blood pressure. Women who smoke at a higher risk of getting CHD than men
➢ Stop or limit your alcohol intake
RISK FACTORS
➢ High blood pressure, smoking, Diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high cholesterol, poor diet, excessive alcohol, depression
RISK ASESSMENT TESTS AND DIAGNOSIS
➢ Check family history on blood pressure and diabetes
➢ Check and record your blood pressure level three times daily over a period of a week
➢ Blood tests:
o Lipid profile to assess cholesterol levels
o Cardiac enzyme test to check for any recent heart muscle damages
o HBA1C to assess to assess the average plasma glucose concentration
➢ ECG (electrocardiogram) which records the electrical activity of the heart
➢ ECHO(echocardiogram) which identifies the structure and pumping function of your heart, thickness of the heart muscle and movement of each heart valve
➢ Coronary angiography which is done at the end stages of diagnosis, is a cardiac catheter test that using a dye, helps to see blockages of arteries, pressures inside the heart chamber and how well your heart is functioning
➢ Myocardial perfusion scan, also done at the end stages of diagnosis, shows the flow of blood to the muscular walls of the heart with the use of a small amount of isotope (radioactive substance) that is injected to your blood